An Agent of Record (AOR), also called a broker of record, is a licensed insurance professional or entity that represents your insured company in managing employee benefits, insurance policies, and compliance requirements, providing you with specialized expertise while reducing administrative burden.
Additionally, an AOR may help evaluate and select a company’s employee benefits, including health insurance, life insurance, and retirement plans.
As remote work continues to expand globally, having an AOR has become increasingly valuable for companies seeking to provide competitive benefits packages while navigating complex regulatory landscapes across multiple jurisdictions.
This relationship is formalized through an Agent of Record letter, which authorizes the AOR to act on your behalf with insurance carriers. Once established, the AOR becomes your company's exclusive representative for managing specified insurance policies and employee benefits programs.
For organizations with remote or distributed teams, an AOR provides critical expertise in navigating the complex landscape of benefits administration across different regions, ensuring compliance while optimizing your benefits strategy.
What does an agent of record do?
An AOR handles benefits strategy development, insurance carrier negotiations, compliance management, employee enrollment, ongoing administration, claims support, and market analysis. These responsibilities are listed in detail below.
Benefits strategy development: The AOR works with your HR team to design comprehensive benefits packages that align with your company's goals, budget, and employee needs, particularly for distributed teams.
Insurance carrier negotiations: Your AOR leverages their industry relationships and market knowledge to negotiate favorable terms, rates, and coverage options with insurance providers.
Compliance management: AORs ensure your benefits programs comply with relevant regulations across different jurisdictions, helping you avoid costly penalties and legal issues.
Employee enrollment: They manage the enrollment process, providing educational resources and support to help employees understand and select appropriate coverage options.
Ongoing administration: AORs handle day-to-day administrative tasks related to your benefits programs, including policy updates, documentation, and carrier communications.
Claims support: When employees encounter issues with claims or coverage, your AOR serves as an advocate, helping to resolve problems efficiently.
Market analysis: AORs continuously monitor the insurance marketplace to identify opportunities for improving your benefits offerings or reducing costs.
🎯 Pro Tip: When selecting an AOR, prioritize those with specific experience in your industry and the regions where your employees are located. This specialized expertise can significantly enhance the value they provide, especially for companies with globally distributed teams.
Why do companies hire AORs?
Companies increasingly turn to Agents of Record to oversee the complexities of benefits administration, particularly as workforces become more distributed. The primary motivation is often to gain access to specialized expertise without expanding internal HR capabilities.
For growing organizations, managing benefits across multiple jurisdictions can quickly become overwhelming. An AOR provides a scalable solution that adapts to your company's evolving needs while maintaining consistent quality and compliance.
Many businesses also recognize the strategic advantage of working with an AOR who has established relationships with insurance carriers. These connections often translate into better coverage options, more competitive rates, and enhanced service levels that would be difficult to achieve independently.
Additionally, companies value the time and resource savings that come with outsourcing benefits administration. By delegating these responsibilities to an AOR, internal teams can focus on core business activities rather than getting bogged down in insurance paperwork and compliance details.
How does the AOR process work?
The AOR process starts once you decide to work with a specific agent and typically takes about 10 days to complete.
Phase 1: The new agent sends an AOR letter that includes your company name, carrier name, policy number, and effective date.
Phase 2: You review the form, place it on company letterhead, sign and date it, then return it to the agent.
Phase 3: The agent submits the signed AOR letter to your insurance carrier.
Phase 4: The carrier processes the transfer within 5–10 days, unless they receive a rescinding AOR from the current agent signed by the policyholder.
If a company changes its mind about the agent of record, it must sign a rescinding letter within five to 10 days to void the old AOR. After that period, the company must sign a new AOR letter to officially appoint a different agent.
Once the insurance carrier accepts the AOR letter, your new agent of record relationship begins, and all previous contracts are considered null and void.
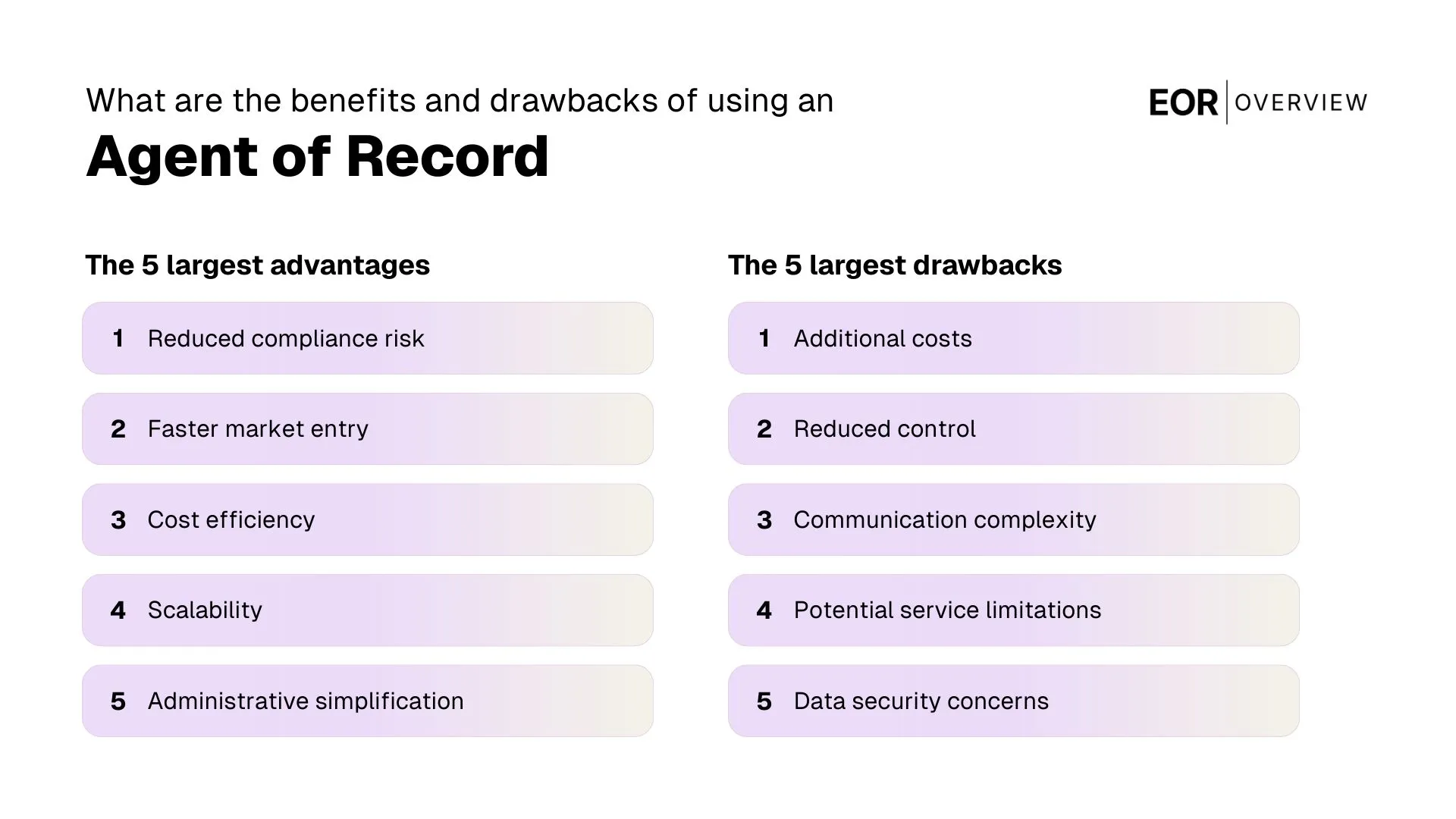
What are the benefits of having an AOR?
The advantages include specialized expertise, time and resource savings, enhanced negotiating power, improved compliance, strategic guidance, employee support, and scalability. These benefits are listed in detail below.
Specialized expertise: AORs bring deep knowledge of insurance markets, benefits administration, and regulatory requirements that most companies don't have internally.
Time and cost savings: By outsourcing benefits administration to an AOR, your HR team can focus on strategic initiatives rather than getting bogged down in paperwork and carrier communications.
Enhanced negotiating power: AORs typically have established relationships with multiple carriers and can leverage these connections to secure better terms and rates than you might obtain independently.
Improved compliance: With regulations constantly evolving, AORs help ensure your benefits programs remain compliant across all jurisdictions where you have employees.
Strategic guidance: Beyond day-to-day administration, AORs provide valuable insights to help you develop benefits strategies that attract and retain top talent in a competitive market.
Employee support: AORs often provide direct assistance to employees with questions or issues related to their benefits, improving the overall employee experience.
Scalability: As your company grows and expands into new regions, an experienced AOR can adapt your benefits strategy accordingly, providing a scalable solution for global workforce management.
Many companies report significant improvements in both the quality of their benefits offerings and administrative efficiency after partnering with an AOR. The combination of specialized expertise and dedicated resources often delivers value that exceeds the cost of the service.
What are the possible drawbacks of having an AOR?
While the benefits of working with an Agent of Record are substantial, it's important to consider potential drawbacks before making a decision. Understanding these challenges can help you select the right partner and establish appropriate expectations.
Additional cost: Hiring an AOR represents an added expense, though this is often offset by savings from improved rates and administrative efficiency. If you terminate your contract in the middle of a policy term, an AOR may charge fees for any remaining or missed payments.
Dependency concerns: Relying heavily on an external partner for critical functions can create vulnerability if the relationship deteriorates or the AOR's service quality declines.
Potential conflicts of interest: Some AORs may have financial incentives to recommend certain carriers or plans, potentially affecting their objectivity.
Transition challenges: Switching to a new AOR can be disruptive, requiring significant time and effort to transfer knowledge and establish new processes.
Communication barriers: Adding another layer between your company and insurance carriers may occasionally complicate or slow down communication.
Variable service quality: Not all AORs provide the same level of service, and it can be difficult to evaluate performance until after you've established the relationship.
To mitigate these potential downsides, thoroughly vet prospective AORs, establish clear performance expectations, and maintain appropriate oversight of the relationship. Many companies find that a well-structured AOR arrangement minimizes these risks while maximizing the benefits.
What is an agent of record letter?
An Agent of Record (AOR) letter is a formal document that authorizes a specific insurance agent or broker to act on behalf of your company in dealings with insurance needs. This letter serves as the official designation of your chosen representative and is recognized by insurance companies as confirmation of the broker's authority to act on your behalf. It is also needed when a business wants to replace an existing AOR and appoint a new agent of record.
The AOR letter typically includes several key elements: your company's information, the designated agent's details, policy number, the effective policy date of the authorization, and an authorized signature from your company. Once submitted to insurance carriers, this letter grants your AOR access to information about your existing policy details and the ability to negotiate on your behalf.
It's important to note that an AOR letter supersedes any previous broker relationships for the specified policies. When you submit a new AOR letter, it effectively terminates the authority of any previous broker and transfers that authority to your newly designated representative.
Most AOR letters remain in effect until explicitly revoked or replaced, though some may include specific termination dates. Understanding these terms is crucial when establishing or changing your broker relationships.
What factors should I consider before signing an AOR letter?
Before formalizing an AOR relationship, it's essential to conduct thorough due diligence. Start by evaluating the agent's experience with companies similar to yours in size, industry, and geographic distribution. An AOR familiar with your specific challenges will provide more relevant guidance and solutions.
Review the scope of services included in the agreement. Some AORs offer comprehensive support encompassing strategy development, implementation, and ongoing administration, while others may provide more limited services. Ensure the scope aligns with your company's needs and expectations.
Compensation structure: Understand how the AOR is compensated (commissions, fees, or both) and whether this creates potential conflicts of interest.
Service guarantees: Look for specific commitments regarding response times, reporting frequency, and performance metrics.
Team composition: Identify the specific individuals who will be handling your account and assess their qualifications and experience.
Technology capabilities: Evaluate the AOR's technology platform and how it will integrate with your existing systems.
References and reputation: Speak with current clients, particularly those with similar profiles to your organization.
Termination provisions: Review the process for ending the relationship if necessary, including notice periods and transition support.
Remember that signing an AOR letter establishes an important business relationship that will impact your employees' benefits experience. Taking time to carefully evaluate potential partners can prevent costly mistakes and disruptions down the road.
Why would I terminate an AOR agreement?
There are several legitimate reasons why companies choose to end their relationship with an Agent of Record. Understanding these common scenarios can help you recognize when it might be time to change insurance agents in your own benefits management strategy.
Performance issues are among the most frequent catalysts for termination. If your AOR consistently fails to meet service expectations, provides inaccurate information, or misses important deadlines, these shortcomings can significantly impact your benefits program and employee satisfaction.
Strategic misalignment: As your company evolves, you may find that your AOR's approach no longer aligns with your benefits philosophy or business objectives.
Expertise gaps: Expansion into new markets or the addition of complex benefit types might require specialized knowledge that your current AOR lacks.
Communication breakdowns: Persistent communication issues or unresponsiveness can erode trust and effectiveness in the relationship.
Cost concerns: If you discover that your AOR's compensation is significantly higher than market rates or that promised cost savings haven't materialized, you may seek a more cost-effective alternative.
Organizational changes: Mergers, acquisitions, or significant restructuring might necessitate a different approach to benefits management.
Compliance failures: Errors or oversights in regulatory compliance can create serious legal and financial risks, potentially necessitating an immediate change.
When terminating an AOR relationship, it's important to follow proper protocols. This typically involves providing written notice according to the terms specified in your agreement and designating an agent of record change before the termination takes effect to ensure continuity in your benefits administration.
Do I need an AOR for my global team?
When selecting an AOR for a global team, look for firms with established international networks or partnerships. The ideal partner should have both broad global capabilities and deep local expertise in your key markets. They should also offer technology solutions that can accommodate multi-country administration and reporting.
The value of an AOR increases with the number of countries where you have employees. Managing relationships with multiple local insurance providers, understanding compliance requirements in each jurisdiction, and coordinating consistent administration becomes exponentially more difficult as your global footprint expands.
International benefits management presents unique challenges, including navigating diverse regulatory environments, understanding country-specific market practices, and addressing varied employee expectations. A globally experienced AOR brings specialized knowledge of these complexities and can help develop a cohesive benefits strategy that works across borders while respecting local requirements.
For companies with internationally distributed teams, the question of whether to engage an Agent of Record takes on additional complexity. The short answer is that while not always legally required, having an AOR with global expertise can provide significant advantages when managing benefits across multiple countries.
For smaller companies just beginning international expansion, a globally-minded AOR can provide valuable guidance on market entry strategies and help establish scalable benefits frameworks that will support future growth across regions.
What is the difference between EOR and AOR?
While both Employer of Record (EOR) and Agent of Record (AOR) services support companies with distributed workforces, they serve fundamentally different functions. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for determining which solution best addresses your specific needs.
An Employer of Record (EOR) becomes the legal employer of your workers in countries where you don't have an entity. The EOR handles payroll, tax withholding, employment contracts, and compliance with local labor laws. Your company maintains day-to-day direction of the employees' work, while the EOR manages the legal and administrative aspects of employment.
In contrast, an Agent of Record (AOR) focuses specifically on insurance and benefits administration. The AOR represents your company in dealings with insurance carriers but does not become the legal employer of your team members. Your company remains the employer of record and maintains responsibility for all other aspects of the employment relationship.
Aspect | Agent of Record (AOR) | Employer of Record (EOR) |
Primary function | Manages insurance and benefits programs | Serves as legal employer |
Employment relationship | No direct employment relationship with your team | Legally employs your team members |
Scope of services | Insurance and benefits administration | Comprehensive employment services including payroll, taxes, and compliance |
Legal responsibility | Limited to benefits compliance | Full employment law compliance |
Typical use case | Companies seeking specialized benefits expertise | Companies expanding internationally without local entities |
Many companies with global teams utilize both services simultaneously. For example, you might engage an EOR to employ team members in countries where you don't have entities, while partnering with an AOR to optimize your global benefits strategy across all locations, including those where you employ people directly.
⚠️ When selecting an Agent of Record, carefully review the terms of the AOR letter and agreement. Pay particular attention to exclusivity provisions, termination clauses, and service guarantees to ensure the relationship can evolve with your company's changing needs.benei
